List of APIs that can be used with the QUERY function
So far, we have practiced how to use and apply the QUERY function.
QUERY(データ, クエリ, [見出し])The QUERY function uses the query language of the Google Visualization API to query the entire data.
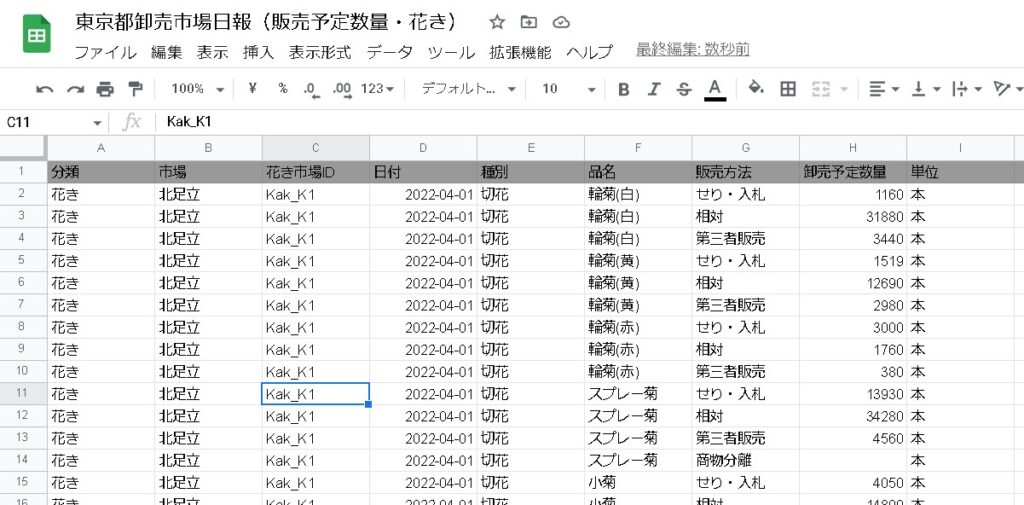
This time, I will summarize the “Query language of the Google Visualization API” as a summary so far.
Here is the official document ▼

Query Language Reference (Version 0.7) | Charts | Google Developers

Language Clauses
Query functions can use the following query language.
| Clause | Usage |
|---|---|
select | Selects which columns to return, and in what order. |
where | Returns only rows that match a condition. |
group by | Aggregates values across rows. |
pivot | Transforms distinct values in columns into new columns. |
order by | Sorts rows by values in columns . |
limit | Limits the number of returned rows. |
offset | Skips a given number of first rows. |
label | Sets column labels. |
format | Formats the values in certain columns using given formatting patterns. |
options | Sets additional options. |
from | The from clause has been eliminated from the language. |
You can do so many things!
SELECT * (column selection)
You can use select to select a range. An asterisk extracts all columns, and specifying a column name extracts the specified column.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select *")=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select A")=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select A,B,C")=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select C,B,A")where
You can specify conditions by using where.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select * where F = 'スプレー菊'")When specifying multiple items, use “and” to connect them.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select * where B='板橋' and F='スプレー菊'")With WHERE OR, you can specify multiple conditions (○○ or ○○).
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select * where B='板橋' or B='スプレー菊'")group by
Aggregates columns together.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select F,count(F) where F is not null group by F")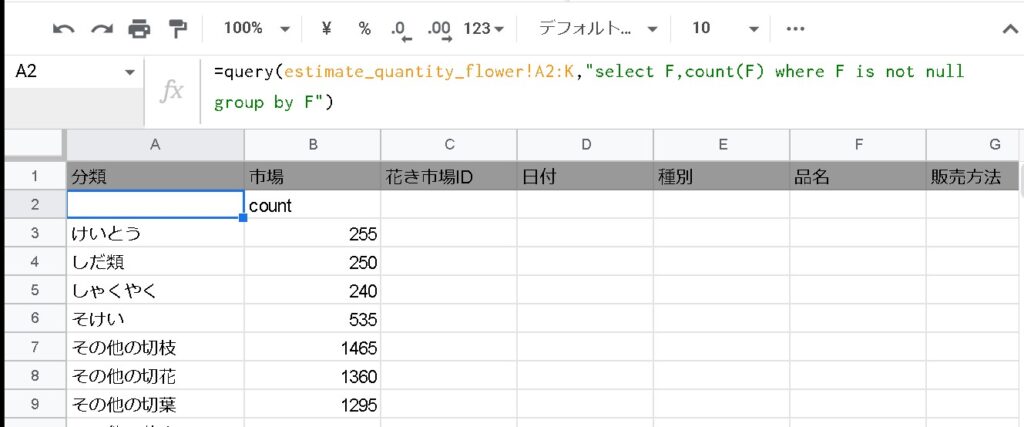
Let AVG(F) where count(F) is to get the average. sum(F) will get the sum of the group. You can get the maximum value with max(F) and the minimum value with min(F).
pivot
You can use pivot.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select F,count(F) where F is not null group by F pivot G")You can output the G column as a pivot.
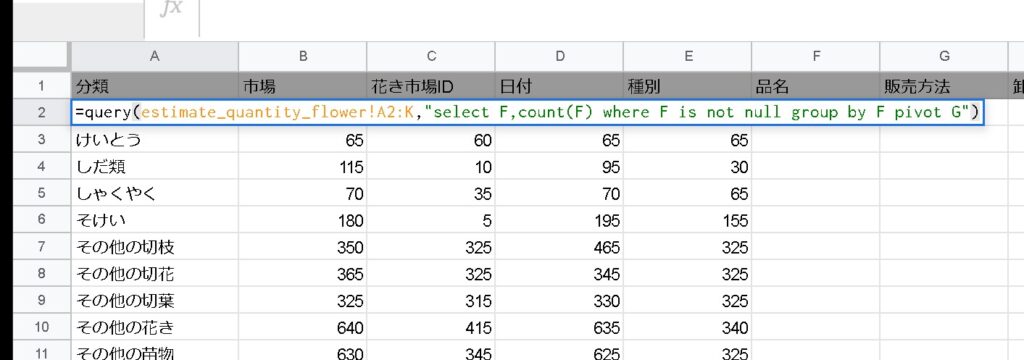
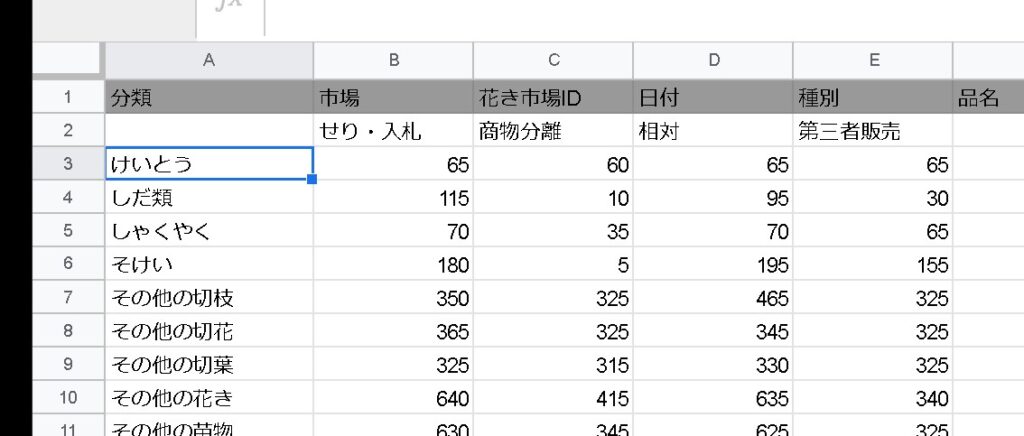
limit
You can limit the number of lines to output. For example, you can limit it to “up to 3 lines”.
=query(estimate_quantity_flower!A2:K,"select * limit 3")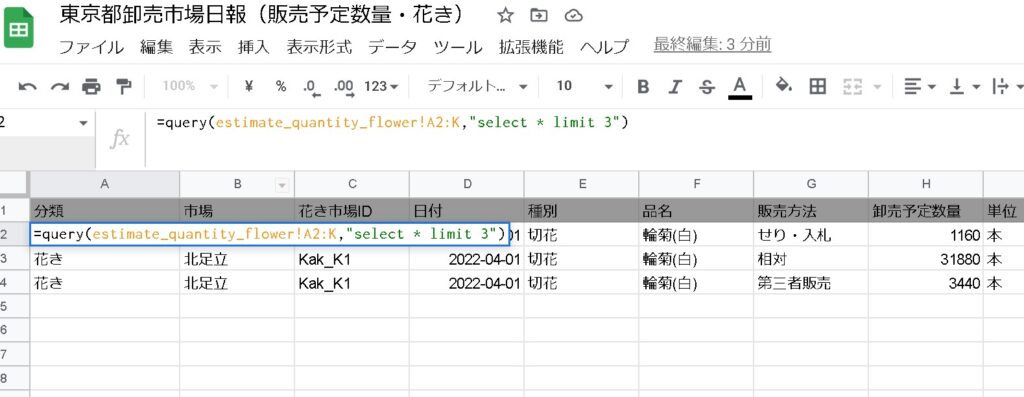
offset
You can skip a specified number of lines by using offset. For example, if you want to skip 10 lines before extracting, set offset 10.
=QUERY(範囲, "offset 数")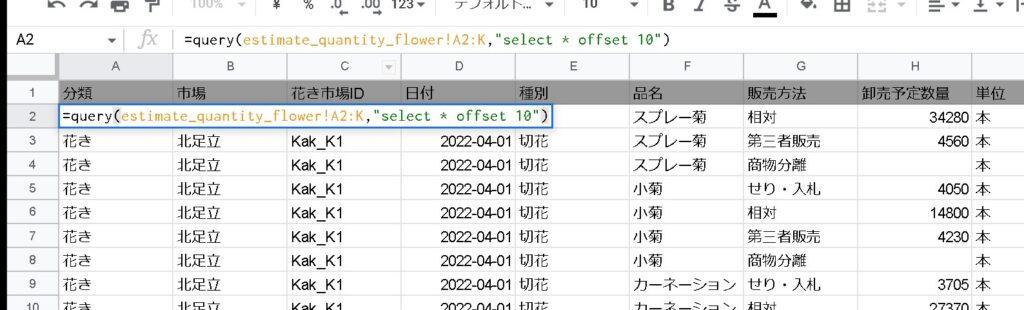
labels
Labels can be displayed in the column header row.
=QUERY(範囲, "label 列 '名前' ")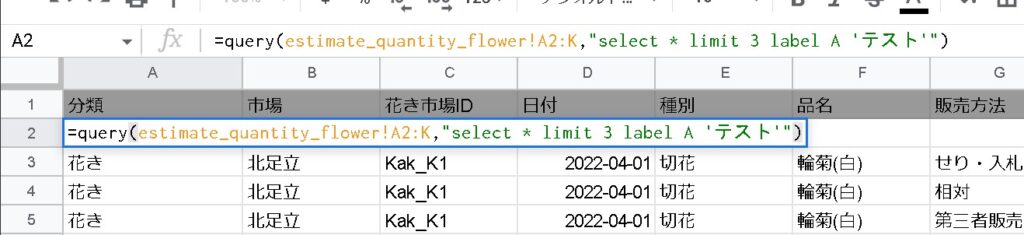
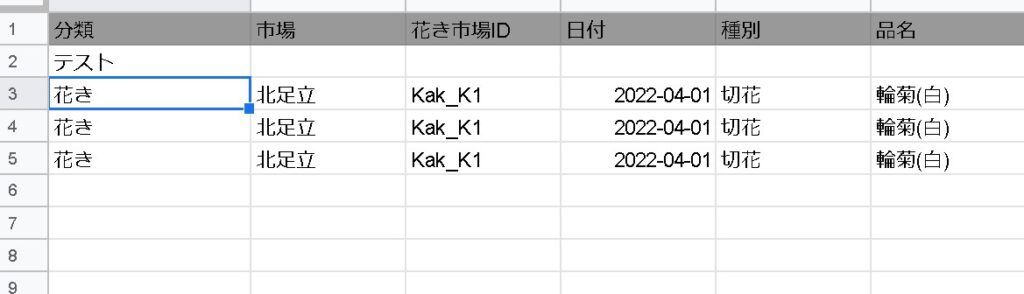
When labeling multiple columns, separate them with commas.
=QUERY(範囲, "label 列 '名前',列2 '名前' ")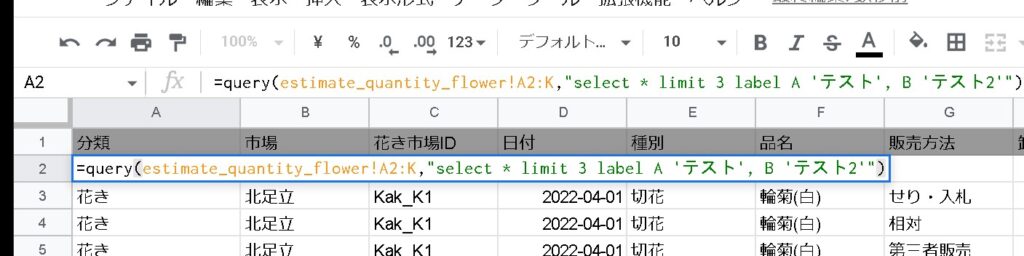
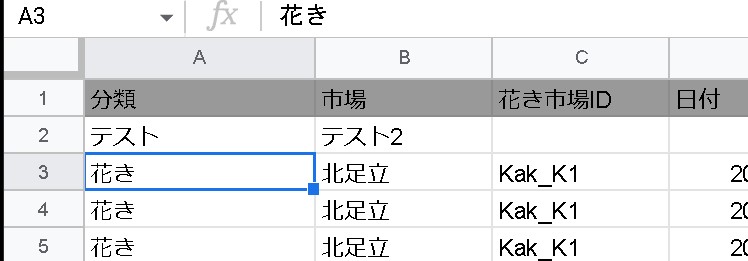
It can also be combined with group by to override the label of the grouped items.
format
format can change the display format.
=QUERY(データ範囲,”FORMAT 列 '書式形式'”)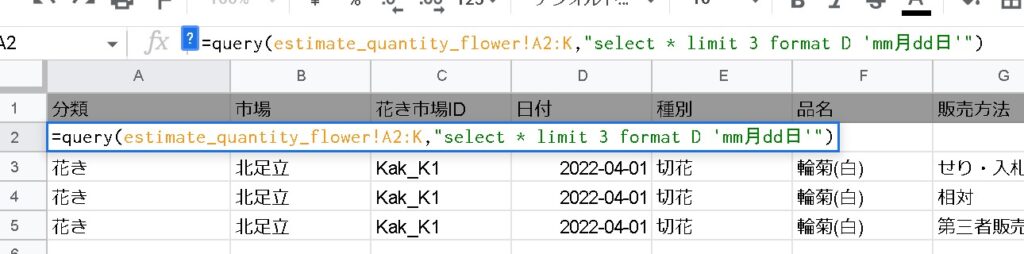
=QUERY(データ範囲,”FORMAT 列 'mm月dd日'”)Converted to mm-month-dd-day format.
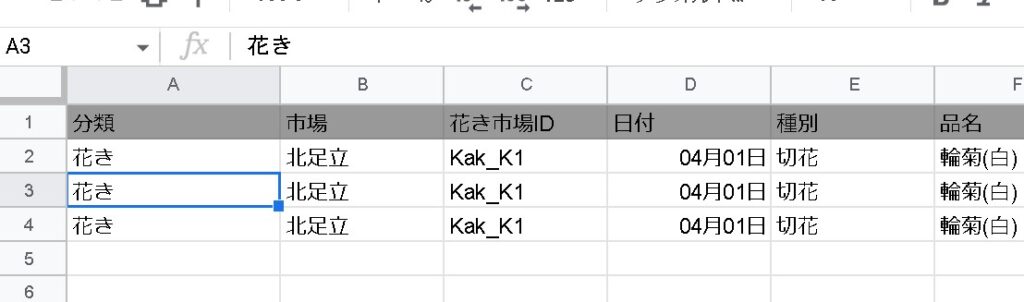
options
Further queries are possible with additional options. You can use order by to sort the order of the specified columns in ascending or descending order.
=QUERY(範囲 "order by 列 asc")=QUERY(範囲 "order by 列 desc")from
*The from clause seems to have been removed from the language.

Query Language Reference (Version 0.7) | Charts | Google Developers

QUERY reserved word list/summary
The following reserved words must be enclosed in backquotes when used as identifiers:
- and
- asc
- by
- date
- datetime
- desc
- false
- format
- group
- labels
- limit
- not
- offset
- options
- or
- order
- pivot
- select
- time of day
- timestamp
- true
summary
By using the “query function” like this, you can extract data under various conditions! I have written several articles on how to use query functions, so please refer to other pages as well.
People can become stronger when they acquire skills.
